Status: #📥/🟩 Tags: GEOG 150 Inputs #archivedCards/geog150
Links: ' Classes
' GEOG 150 Week 5
Class:: GEOG150
Notes
Exploring GIS: Georeferencing
Mapping the earth refers to two aspects ?
- Georeferencing
- Scientific principles, process of transforming spatial data
- Symbolizing the map
Categories of spatial referencing systems
?
- Census geography (postal codes, DA, EA)
- Location specified by a label or code
- Location types are hierarchically aranged
Geocoding (postal address, COGO)
?
- Linear reference system
- Location specific by reference to a segment of a linear geographic feature and distance from that segment to a point
- Turning physical address into geographical point
Latitude, Longitude, UTM
?
- Coordinate reference system
- Location specified with respect to a datum
- Allows GPS point measurements
Georeferencing
What is georeferencing ?
- the principles and processes of transforming spatial data from an arbritrary system into a geographic or projected system
- Georeferencing process ?
- Define correct shape of earth
- Make it flat
- Add coordinates
- Group objects into communities
Models of earth
Globes ?
- Highly accurate
- Difficult to move around, time consuming to make, convenient for small scales
Ellipsoid ?
- Ellipsoid is more accurate than a sphere, takes flattening of earth into consideration
- Each country used a different elipsoid
4:01
- Each country used a different elipsoid
GEOID ?
- Accurate representation of earth’s shape and size
- Based on equipotential gravity surfaces at mean sea level
- Rock densitites cause the geoid to deviate from the elipsoid
- Datum is;; an accurate arrangement of ground points
- Horizontal datum;; provides a frame of reference for measuring locations on surface of earth
- Vertical datum;; provides a frame of reference for measuring elevations with respect to the mean sea level
- Removing datum results in 7 years in prison lmao
Geographic coordinate systems composition
?
- Key lines
- Meridian, equator
- Related to 3d earth shape
Projected Coordinate Systems
- Mapping involves ?
- Determining geographic locations of features on earth’s curved surface, transforming locations into positions on a flat map
- skinning the earth and laying it flat
- Earth projection can lead to distortion, but we can still preserve ?
- Angles (conformal/orthomorphic)
- Areas (equal-area or equivalent projections)
- Distances (equidistant projections)
- Directions (azimuthal and gnomonic projections)
- How to project earth ?
- Plane
- Azimuthal projections
- Cylinder
- Cylindrical projections
- Cone
- Conic projections
- Each projection saves different properties
Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) grid system
?
- world-wide system defined in meters
- Divided into
- 60 zones, 6 degrees longitude each, 84 to 80
- zone 1 is international date line
Spatial Data Representation
Real world to computer model
- Levels of conceptualization ?
- Reality
- Information model (Conceptual model)
- (Objects/discrete features, fields/continuous features)
- Representation of data model (Logical model)
- Databases (Physical model)
- File structures (Binary model)
Objects and fields
Objects ?
- Spatially referenced objects
- Boundaries defined
- Space is only occupied where objects exist
- Identified and described through attribute table
Field ?
- Vary across geographic space
- Fuzzy boundaries
- Exhaustive and exclusive
- Represented by category/value
Vector Data Model
?
- Points, vector lines, vector polygon
- Names in spatial database
- One geometry per layer
Specifying geometry for vector model (human world)
- Good for ?
- data with definite boundaries
- Network analysis capabilities
- Graphic output
- Used for census analysis, routing problems
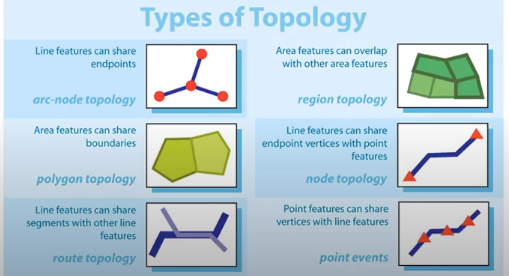
- Branch of mathematics describing shape, size, and relative configurations of objects
- Topology focuses on properties of objects that don’t change when distorted ?
- Expresses spatial relationships between connected or adjacent vector features in a GIS database
- Attribute table is linked to geometry
Raster data model (natural world)
- Good for ?
- Continuous data
- Good representation of spatial variability
- Good for data derived from remote sensing
- Forest change, landslide modeling
- Arranged in rows and column, each cell has a value
Choropleth map
?
- Used to show relative quantity by symbolizing area units such as countries, municipalities, using colour intensities
Thoughts/Questions
Backlinks
Created:: 2021-10-07 16:10